Table of Contents
What is Data Mining?
- Data Mining is the process of sorting large data sets to find relevant and valuable information for a specific purpose.
- As a sub discipline of computer science, Data Mining focuses primarily on patterns.
- After the data has been obtained and stored, the next step focuses on its interpretation; otherwise, it would be a pointless task of Data Mining.
- Data analysis uses concepts like machine learning.
- In which complex adaptive algorithms analyze data artificially.More traditional methods involve the participation of data scientists (experts specifically trained to interpret complex information).
- Who is responsible for generating reports for management to make decisions.
Knowledge management for customers
Knowledge Management for Clients refers to a company’s tools and processes to capture, store, organize, access, and analyze customer data to boost sales, holding, and engagement efforts.
What uses can be given to data mining?
- Data mining used for many purposes, depending on each company and its needs.
Some of Data Mining possible uses include the following:
Forecasts and risks:
- Analyzing data to determine the source of past mistakes
- For example, the number of web visitors who did not purchase a particular item after browsing it
- Similarly determining the time of day that a system experienced web traffic overload in the past.
- It can help by allocating more resources or investing in server upgrades.
Grouping:
- Customer-supplied data allows companies to group users in many ways.
- For example, demographically based on gender, age, income, where they live, and their spending habits.
Behavioral Analysis:
- Examining the data allows companies to understand the type of stimuli.
- Do certain groups respond to specific offers or emails at a particular time of day or on a specific day of the week.
- Data Mining is the process of databases to find helpful information for decision-making.
- The fundamental basis for this is that these patterns help decision-making.
- For example, it could help companies understand their customers’ behavior patterns to facilitate the establishment of strategies to increase sales or reduce costs.
Advantages of Data Mining:
- The fundamental advantage of this data analysis process is the large number of business scenarios.
Prediction:
- Forecast of the company’s sales.
Probability:
- Selection of the best clients for direct contact either by phone or email.
Sequence analysis:
- Analysis of the products that customers have bought and check the interrelation between them.
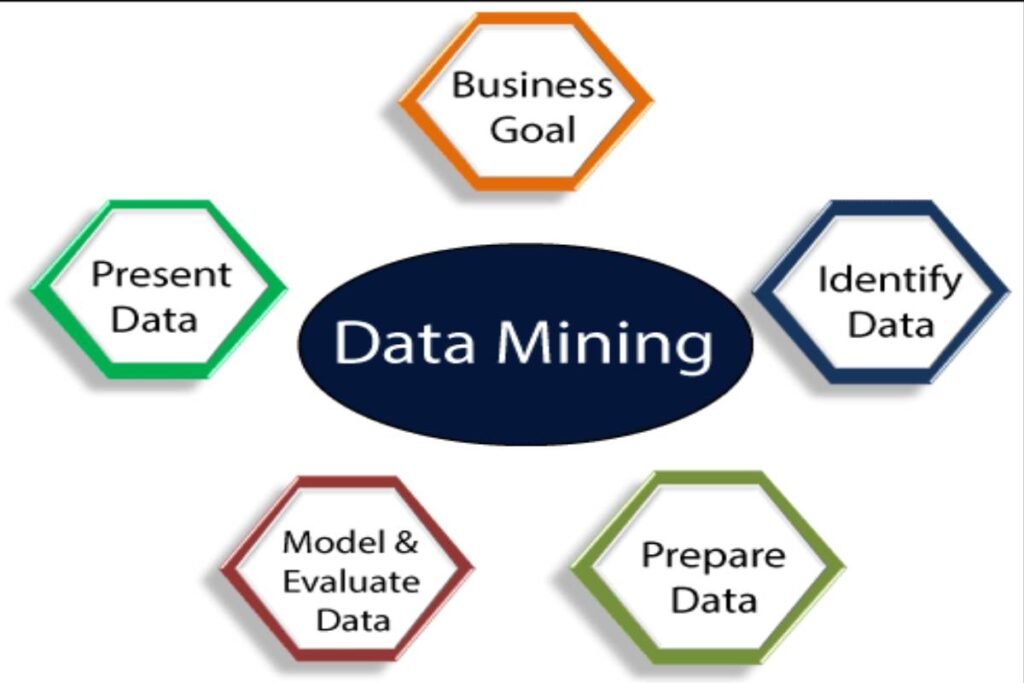
What are different Stages of Data Mining?
- Within a Data Mining process, we can find five phases:
Objective and data collection:
- First of all, we focus on what type of information we want to obtain.
- Let’s imagine the example that a supermarket wants to know what time of day is where there is more customer attendance.
- Data Mining would be the objective and the information that the trade wants to obtain in this case.
Data processing and management:
- Once we know the data we want to collect, we put the data to work.
- Once the sample is selected
Model selection:
- It is closely related to the previous phase. It is about creating a model or algorithm that gives us the best possible result.
- Data becomes a complicated task since it will depend on the type of information to be analyzed.
- Therefore, data miners carry out different tests of the algorithm.
- Such as linear regression, decision tree, time series, neural network, etc.
Analysis and review of results:
- Basically, it analyzes the results to check if they yield a logical explanation.
- An explanation that facilitates decision-making based on the information provided by the results.
Model update:
- The last step in the process would be the model update.
- We can do it over time so that it does not become obsolete.
- The model variables can also become insignificant, and therefore a periodic control of the model is required.